5-Card Friday
A Bi-Weekly Update from the ITS UX Team

Online Food Shopping During COVID-19
A recent article from NN/g explores the overall user and customer experience of online shopping for food.
Some points in the article: Allow users to reserve delivery windows before they start shopping; clearly communicate delivery minimums and fees; allow users to specify substitutions for low-stock items as they shop.
Online Shopping for Food: UX & CX
1. Users should be told if there are any delivery or pickup times available upfront, before they start shopping. This information should be detailed and accessible to all users, whether they are logged or not.
2. Users should be allowed to reserve a time for their delivery or pickup before they start shopping (or at any time during the shopping process).
3. If the user has specified a delivery time or location, check first that the delivery can be made at that time or location. Alert the user if any of these are unavailable as soon as possible in the shopping process.
Read Full Article
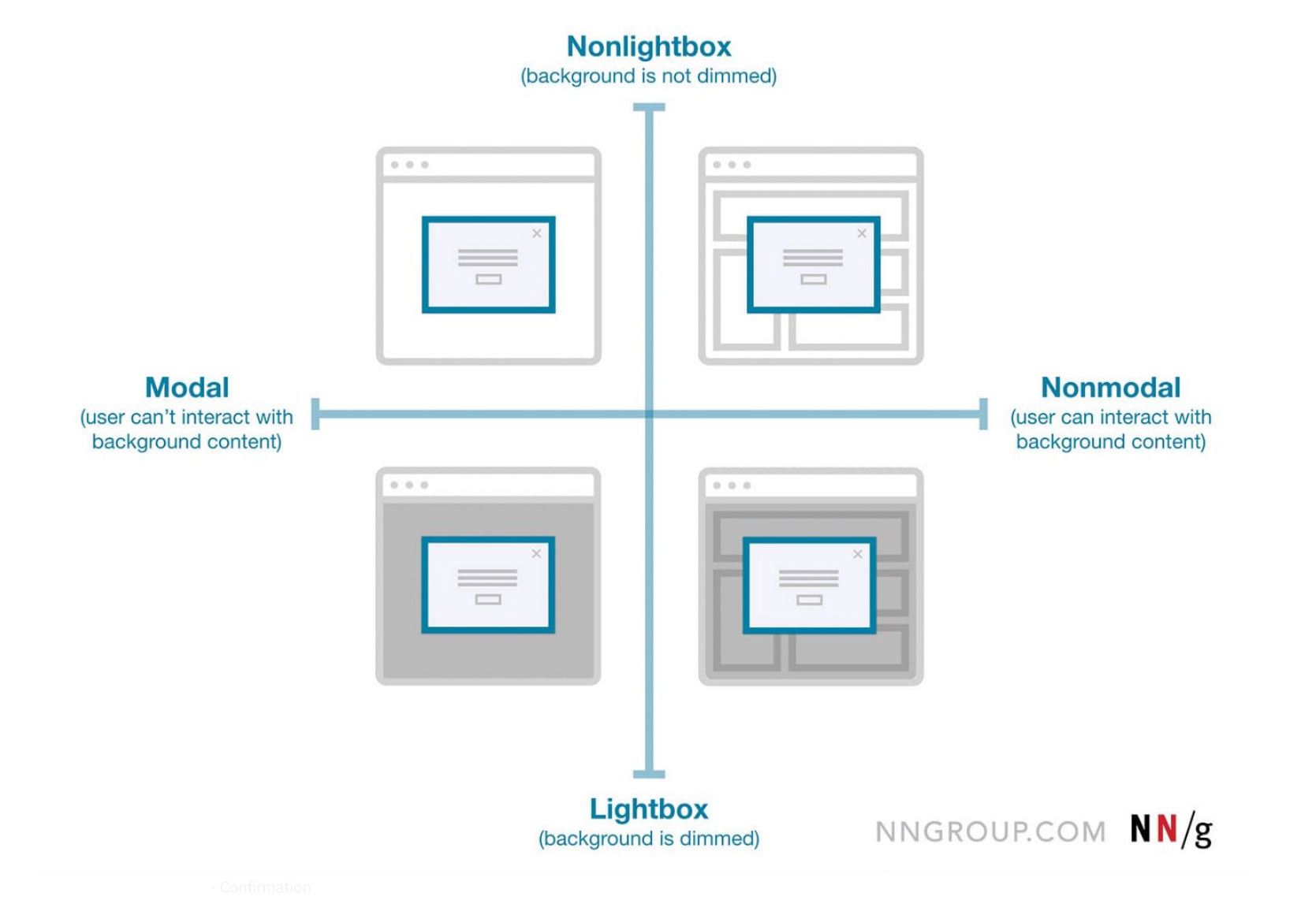
Modals vs. Page: A Decision Making Framework
Ever had someone ask you, “What’s the difference between a modal, an overlay, and a dialog?”. Often they are thought of as the same thing or different only by a technicality.
Flip the card over to learn more about how to decide on using a modal or a page in UX design.
Using Modals vs. Pages
In this article, the author synthesized all the best guidelines, heuristics, and recommendations to create a flowchart that, when applied correctly, will help you to understand whether your design should live in an overlay or not.
Read Full Article

UX Design Glossary: How to Use Affordances in User Interfaces
Do you know what "affordances" are with regards to user interfaces and user experience?
In short, affordances are cues which give a hint how users may interact with something, no matter physical or digital.
Flip the card over to learn more.
Types of Affordances in UI
Affordances in user interfaces can be classified according to their performance and presentation. Anyway, their main goal is to actualize the knowledge and experience people already have to simplify the interaction flow.
Affordances are classified as either explicit (obvious) or implicit (hidden), graphic, copy (language), pattern, animated, negative, or false affordances.
Read the article from UX Planet to learn more.
Read Full Article
UI vs. UX: What’s the difference
UI design and UX design are two of the most often confused and conflated terms in web and app design. And understandably so. They’re usually placed together in a single term, UI/UX design, and viewed from the surface they seem to be describing the same thing.
Flip the card over to learn more.
UI vs UX: What’s the difference
A UX designer decides how the user interface works while the UI designer decides how the user interface looks. This is a very collaborative process, and the two design teams tend to work closely together. As the UX team is working out the flow of the app, how all of the buttons navigate you through your tasks, and how the interface efficiently serves up the information user’s need, the UI team is working on how all of these interface elements will appear on screen.
Read Full Article

The Psychology in UX Design
"A designer who doesn’t understand human psychologies is going to be no more successful than an architect who doesn’t understand physics."
— Joe Leech
Flip the card over to learn more.
The Psychology in UX Design
Psychology is integral part of User Experience(UX) design process. Understanding how the people interact with the product and how their decisions can be influenced or can be manipulated are the topics to be covered by UX designers. Design psychology is a combination of neuroscience, cognitive psychology, social psychology and human computer interaction that approaches user experience design through the lens of human behavior.
UX can take from the following:
- Chameleon Effect/Mirroring
- Priming
- Von Restorff effect
- Serial position effect
- Gestalt Principles
- Cognitive load
- And More...
Read Full Article

